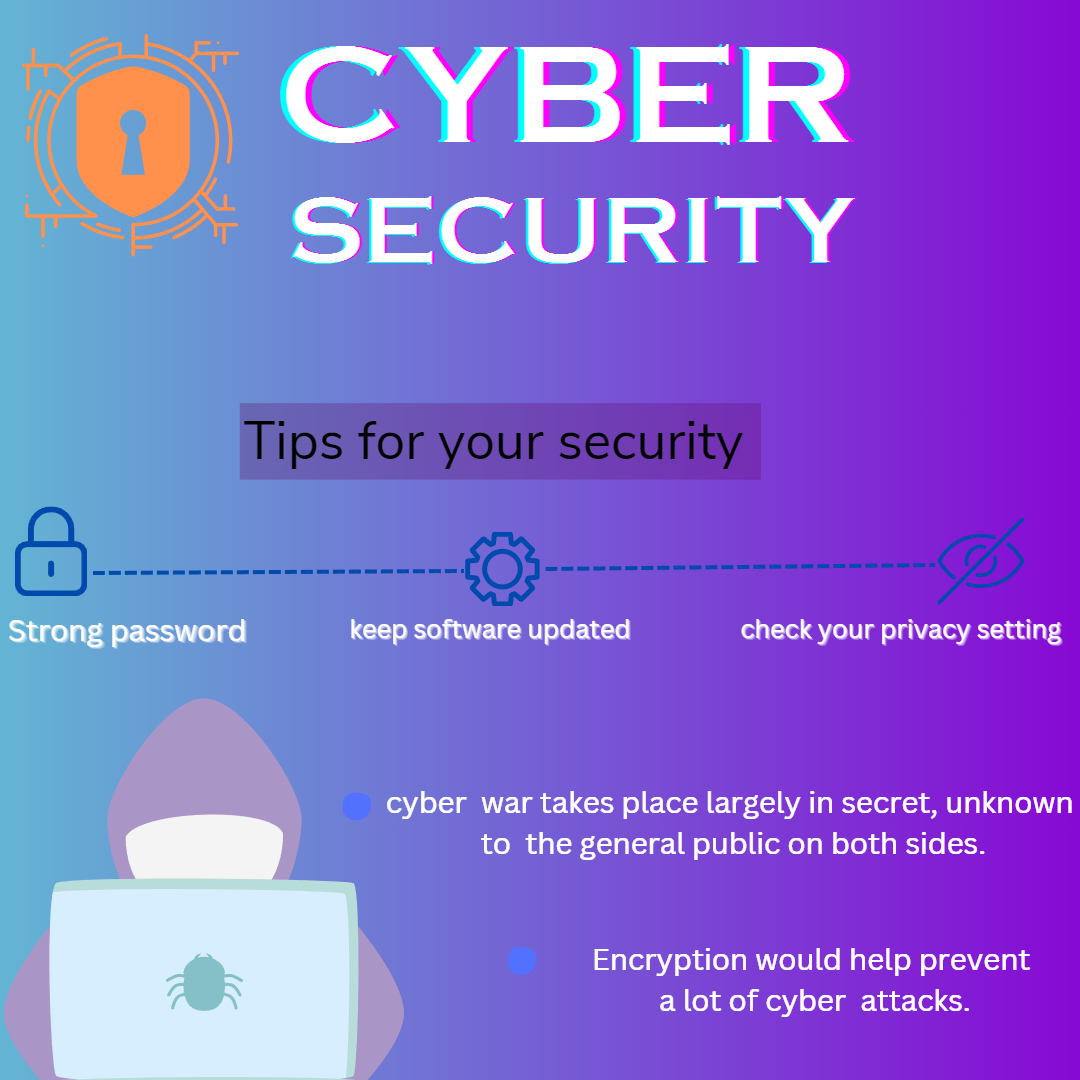
In cybersecurity, “availability” refers to the assurance that systems and data are accessible and usable when needed by authorized users. It is one of the three core principles of the CIA Triad, which also includes confidentiality and integrity.
It involves measures like redundancy, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery to prevent downtime and maintain service continuity. Availability is crucial for uninterrupted business operations, maintaining productivity, and meeting user expectations. Techniques such as load balancing and DDoS protection are employed to ensure systems remain functional and responsive, even under heavy load or during cyberattacks. By prioritizing availability, organizations can avoid costly disruptions and maintain trust and reliability.
Key Aspects of Availability:
Redundancy: Implementing redundant systems and data backups to ensure that services remain available even if one component fails.
Disaster Recovery: Having a robust disaster recovery plan to quickly restore operations in the event of a catastrophic failure, such as a natural disaster or cyberattack.
Fault Tolerance: Designing systems that can continue to operate properly even in the event of the failure of some of their components.
Regular Maintenance: Performing routine maintenance and updates to prevent system downtime due to outdated software or hardware issues.
Load Balancing: Distributing workloads across multiple systems to ensure no single system is overwhelmed, enhancing overall system performance and reliability.
DDoS Protection: Implementing defenses against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which aim to disrupt service availability by overwhelming the network with traffic.
Importance of Availability:
Availability ensures that:
- Business operations continue without interruption, which is critical for maintaining productivity and customer satisfaction.
- Data and resources are accessible to those who need them, when they need them, avoiding costly downtime.
- Trust and reliability are maintained, as users and customers expect consistent access to services and information.
Cyber threats refer to malicious activities aimed at compromising the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information systems and data. These threats are carried out by cybercriminals, hackers, or other malicious actors who exploit vulnerabilities in software, hardware, or human behavior to gain unauthorized access, disrupt services, or steal sensitive information. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity measures.

In summary, ensuring availability in cybersecurity involves a combination of strategies, technologies, and practices aimed at keeping systems and data accessible and operational whenever needed.