several major social media platforms were hit by a significant cyber attack, leading to widespread disruptions. The attack appears to have targeted user data, and there are reports of unauthorized access to personal information, potentially affecting millions of accounts globally.
The breach is notable not only for its scale but also for the sophistication of the techniques used by the attackers. They employed advanced phishing tactics, where fake login pages mimicking legitimate sites tricked users into revealing their credentials. Additionally, some accounts were compromised through vulnerabilities in the platforms themselves, possibly exploiting unpatched security flaws.
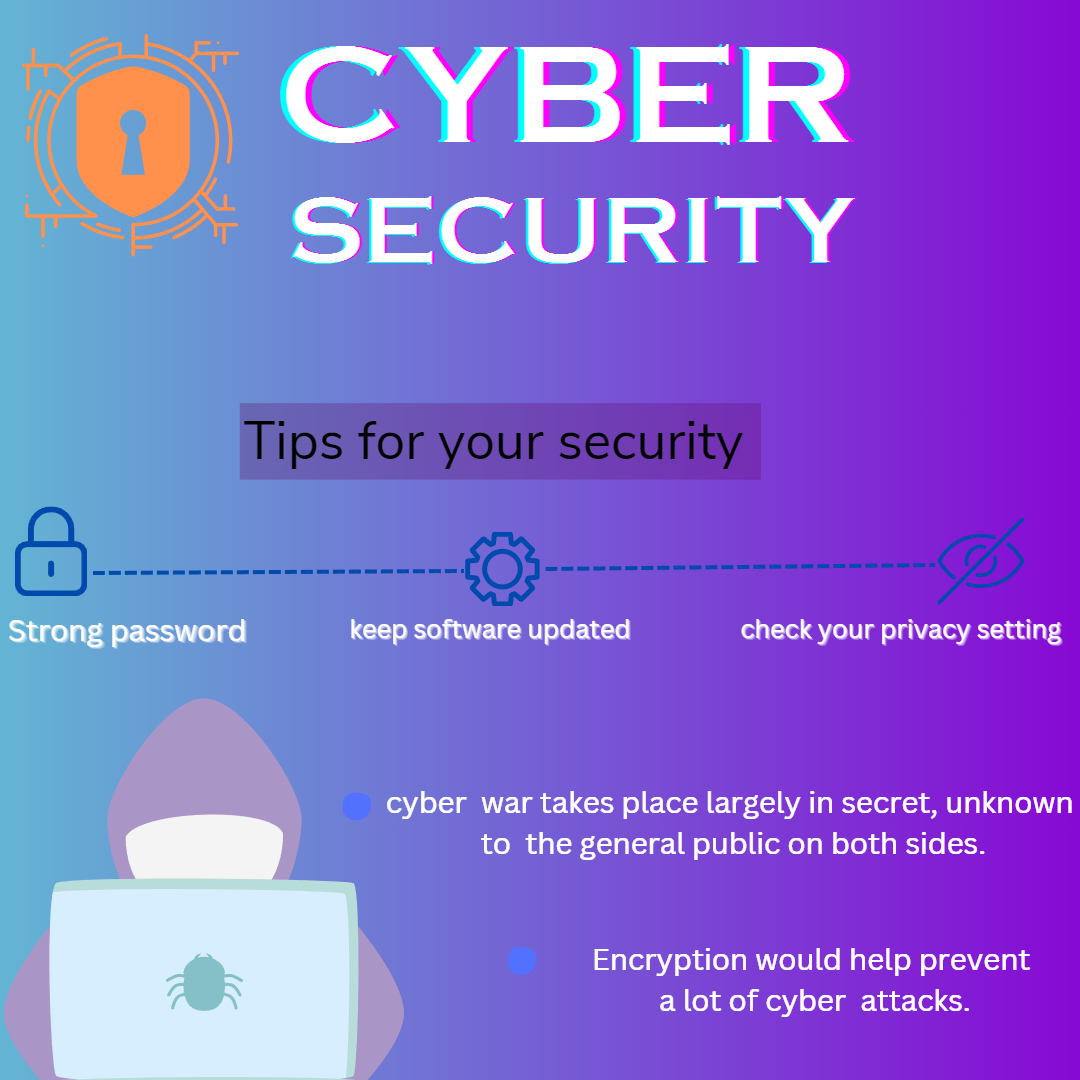
As a result of the attack, users are advised to immediately change their passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and be cautious of any unusual activity on their accounts. It’s also crucial to review account settings and revoke access to any third-party applications that seem suspicious.
Key Concepts of Cyber Attack on Social Media
1. Phishing
- Definition: Phishing involves tricking individuals into revealing their login credentials or other sensitive information by pretending to be a legitimate entity.
- Common Techniques: Attackers often use fake login pages or send messages that appear to come from trusted sources like the social media platform itself.
2. Malware Distribution
- Definition: Social media can be used as a vector for distributing malicious software.
- How It Works: Links, ads, or attachments shared on social media may lead users to download malware, which can steal data or control devices.
3. Social Engineering
- Definition: This refers to manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or taking actions that compromise security.
- Examples: Attackers may impersonate friends or colleagues to gain trust and trick victims into revealing personal details or clicking on malicious links.
4. Account Takeover (ATO)
- Definition: This occurs when attackers gain unauthorized access to a user’s social media account.
- Impact: Attackers can post malicious content, send spam, or carry out scams, potentially leading to reputational damage or further security breaches.
5. Credential Stuffing
- Definition: This is an attack where previously leaked or stolen username/password pairs are used to gain unauthorized access to multiple accounts.
- Why It Works: Many users reuse passwords across different platforms, making it easier for attackers to compromise multiple accounts.
6. Data Breaches
- Definition: Large-scale attacks that result in the exposure of vast amounts of user data, including personal information, messages, and more.
- Consequences: Data breaches can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other forms of cybercrime.
7. Exploitation of Vulnerabilities
- Definition: Attackers may exploit unpatched security flaws in social media platforms or related applications.
- Example: A vulnerability in a social media app’s API could be used to gain unauthorized access to user data.
8. Bots and Automation
- Definition: Bots are automated programs that can carry out repetitive tasks on social media, often used in cyber attacks.
- Usage: Bots can be used for spreading malware, conducting phishing campaigns, or even influencing public opinion by posting large volumes of content.
9. Reputation Damage
- Definition: Damage to an individual’s or organization’s reputation due to unauthorized posts or information leaks from compromised social media accounts.
- Impact: Can lead to loss of trust, legal issues, and financial losses.
10. Legal and Regulatory Ramifications
- Definition: Failure to protect user data can lead to legal consequences, especially with strict data protection laws like GDPR in place.
- Example: Companies may face heavy fines and lawsuits if they fail to secure user data and comply with regulations.
11. Awareness and Education
- Importance: Users and organizations must stay informed about the latest threats and security practices to protect themselves from cyber attacks.
- Best Practices: Regularly updating passwords, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), and being cautious about sharing personal information online.
Cyber attacks on social media have become a growing concern as these platforms hold vast amounts of personal and sensitive data. These attacks typically involve tactics like phishing, where attackers deceive users into providing login credentials through fake login pages or emails. Once attackers gain access to an account, they can perform various malicious activities, including spreading malware, conducting scams, or stealing personal information.
Types of Cyber Attack
1. Phishing Attacks
- Description: Attackers create fake social media login pages or send deceptive messages pretending to be from a trusted source, like the platform itself, to trick users into revealing their usernames and passwords.
- Impact: Successful phishing can lead to account takeover, identity theft, or further exploitation of the user’s connections on the platform.
2. Social Engineering
- Description: This involves manipulating people into giving up confidential information by exploiting human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Attackers may pose as friends, family, or even customer support representatives.
- Impact: Social engineering can lead to unauthorized access to accounts, sensitive data leaks, and financial fraud.
3. Malware Distribution
- Description: Cybercriminals use social media platforms to distribute malware by embedding it in links, ads, or attachments that users are tricked into clicking. These malicious programs can then steal data or control the victim’s device.
- Impact: Malware can compromise not only the social media account but also the entire device, leading to broader security issues, including data theft and ransomware attacks.
4. Credential Stuffing
- Description: Attackers use lists of compromised usernames and passwords from previous data breaches to attempt logins on various social media platforms, relying on the common practice of password reuse.
- Impact: This can lead to unauthorized access to accounts, where attackers can further exploit the compromised data or spread malicious content.
5. Impersonation and Fake Accounts
- Description: Attackers create fake accounts or impersonate real users to deceive others. These accounts can be used to spread misinformation, conduct scams, or trick users into clicking on malicious links.
- Impact: Fake accounts can damage reputations, lead to financial losses, and spread harmful content across the platform.
6. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Description: XSS attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into a webpage viewed by others. On social media, this can occur in comment sections, profiles, or messages, allowing attackers to steal session tokens, perform actions on behalf of users, or redirect users to malicious sites.
- Impact: XSS can lead to unauthorized access to user accounts and the spread of malware without the user’s knowledge.
7. Botnets
- Description: Botnets are networks of compromised computers or accounts controlled by an attacker. On social media, botnets can be used to automate the spread of spam, misinformation, or coordinated attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS).
- Impact: Botnets can amplify attacks, making them more effective and harder to detect. They can also overwhelm social media platforms with traffic, causing service disruptions.
8. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
- Description: In MitM attacks, attackers intercept the communication between a user and the social media platform, often on unsecured networks. They can eavesdrop on conversations, steal credentials, or alter communications.
- Impact: MitM attacks can lead to the exposure of sensitive information, such as login credentials or private messages, which can be used for further attacks.
9. Data Mining and Scraping
- Description: Attackers or malicious entities collect large amounts of data from social media profiles, often without the users’ consent. This data can be used for identity theft, creating fake profiles, or selling on the dark web.
- Impact: Data scraping can lead to privacy violations, targeted phishing attacks, and the creation of fake accounts using stolen data.
10. Exploitation of Vulnerabilities
- Description: Attackers exploit unpatched security flaws in social media platforms or associated third-party applications. These vulnerabilities can allow unauthorized access, data breaches, or even the complete takeover of user accounts.
- Impact: Exploiting these vulnerabilities can result in massive data breaches, loss of trust, and significant financial and reputational damage for both users and the platform itself.
11. Ransomware Attacks
- Description: Although more common in business environments, ransomware can also target social media users. Attackers may lock users out of their accounts or encrypt personal data, demanding payment for the decryption key.
- Impact: Victims may lose access to their accounts and personal data, and even if the ransom is paid, there is no guarantee the data will be recovered.
12. Scams and Fraud
- Description: Cybercriminals use social media to conduct various scams, such as fake giveaways, charity frauds, or romance scams, where they exploit emotional connections to extract money or personal information.
- Impact: Victims may suffer financial losses, emotional distress, and privacy violations.
Consequences of Cyber Attacks :
Here are the consequences of cyber attacks on social media:
Identity Theft: Attackers can steal personal information and use it for identity theft, leading to financial fraud, unauthorized transactions, and damage to credit scores.
Financial Loss: Victims may experience financial loss due to scams, fraudulent transactions, or ransom payments demanded by cybercriminals after an attack.
Reputation Damage: Compromised accounts can be used to post inappropriate content or send spam, damaging the reputation of individuals or businesses, potentially leading to loss of trust and customers.
Privacy Violations: Sensitive data, such as private messages, photos, and personal details, can be exposed, leading to a breach of privacy and potential blackmail.
Spread of Misinformation: Hacked accounts can be used to spread false information or propaganda, influencing public opinion or causing social unrest.
Legal Ramifications: Companies that fail to protect user data may face legal consequences, including fines and lawsuits, especially under data protection regulations like GDPR.
Emotional Distress: Victims of cyber attacks often experience significant emotional distress, including anxiety, fear, and a sense of violation due to the breach of their personal information.
Service Disruptions: Large-scale cyber attacks can lead to service disruptions on social media platforms, affecting millions of users and businesses that rely on these services for communication and marketing.
Loss of Data: Cyber attacks can result in the permanent loss of important personal or business data, especially if it is not properly backed up.
Increased Costs: Organizations may incur significant costs related to incident response, recovery, and improving security measures post-attack.
One of the major risks is Account Takeover (ATO), where cybercriminals gain control of a user’s social media account, often leading to the posting of harmful content or spamming followers, damaging the victim’s reputation. Another common method is credential stuffing, where attackers use previously leaked passwords to gain unauthorized access to multiple accounts, exploiting the common habit of password reuse.

Cyber attacks on social media are increasingly common, posing significant risks to both individuals and organizations. These attacks often involve tactics like phishing, where attackers trick users into revealing their login credentials, or malware distribution, which compromises devices and data through malicious links or attachments. Other common methods include social engineering, where attackers manipulate users to gain sensitive information, and credential stuffing, which exploits reused passwords across multiple accounts. The consequences of such attacks can be severe, leading to identity theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and legal issues. As social media platforms continue to grow in influence, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures becomes ever more critical.