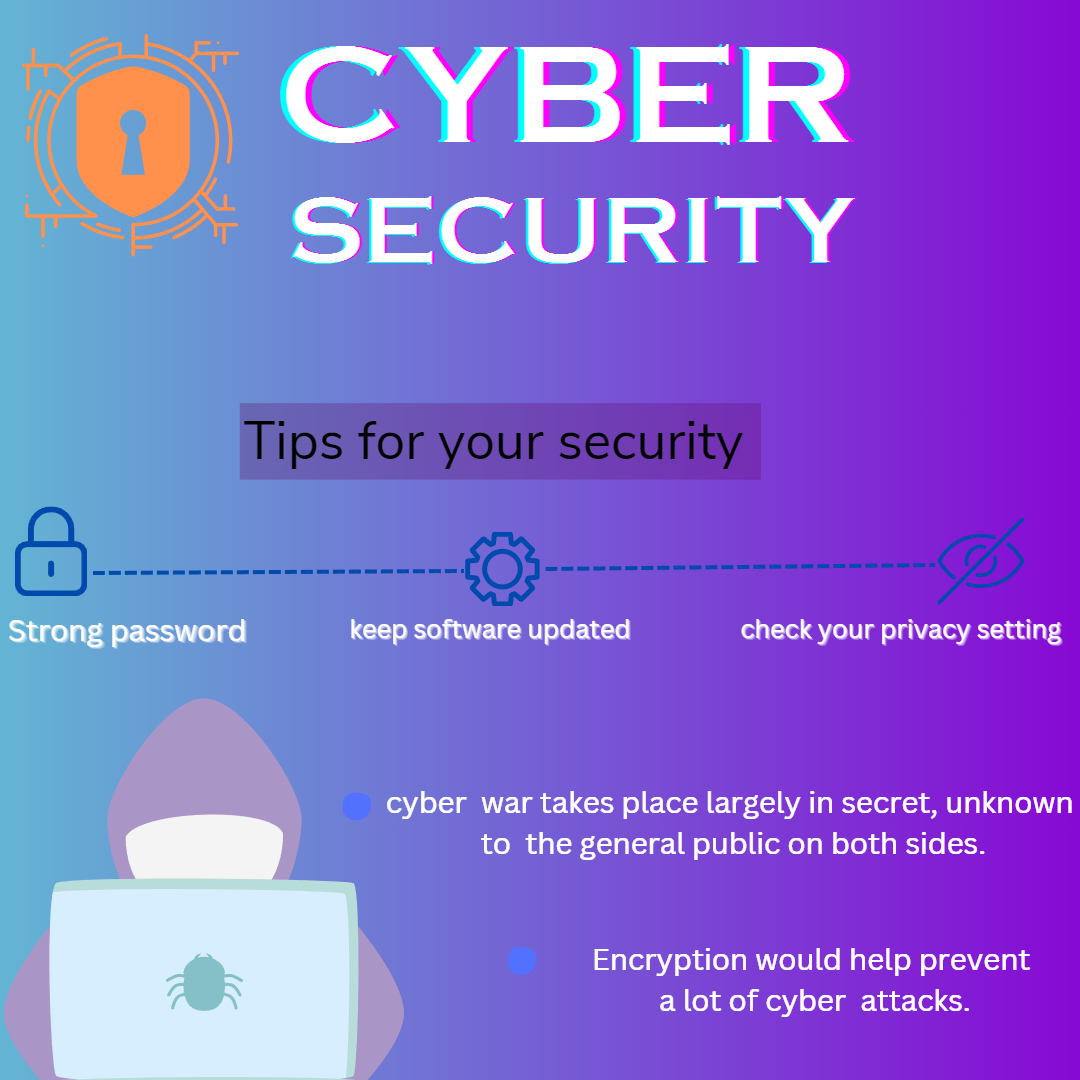
What is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, damage, or theft. It encompasses various technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard digital information and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is essential for businesses, governments, organizations, and individuals to mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats such as malware, phishing, ransomware, hacking, and other cyberattacks. It involves implementing measures like firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and security protocols to defend against these threats.
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field as new technologies emerge and cyber threats evolve in sophistication. It requires ongoing vigilance, proactive risk management, and continuous adaptation to stay ahead of cybercriminals and protect digital assets effectively.
Cybersecurity is a multifaceted discipline dedicated to safeguarding digital systems, networks, and data from various cyber threats. These threats can range from simple nuisances like spam emails to highly sophisticated attacks targeting critical infrastructure or sensitive information. Here’s a more comprehensive explanation:
1. **Threat Landscape**: The digital world is fraught with threats, including hackers, malware, viruses, ransomware, phishing scams, and more. These threats exploit vulnerabilities in software, hardware, or human behavior to gain unauthorized access to systems or data.
2. **Objectives of Cybersecurity**:
– **Confidentiality**: Ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access sensitive information.
– **Integrity**: Protecting data from unauthorized alteration or tampering, maintaining its accuracy and reliability.
– **Availability**: Ensuring that systems and data are accessible to authorized users whenever needed, preventing service disruptions or downtime.
– **Authenticity**: Verifying the identity of users or systems to prevent impersonation or unauthorized access.
– **Non-repudiation**: Ensuring that actions or transactions cannot be denied by the parties involved, providing accountability and traceability.
3. **Key Components of Cybersecurity**:
– **Network Security**: Protecting networks from unauthorized access or attacks through technologies like firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection/prevention systems.
– **Endpoint Security**: Securing individual devices (endpoints) such as computers, smartphones, and IoT devices with antivirus software, encryption, and access controls.
– **Application Security**: Ensuring that software applications are free from vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers, through secure coding practices, testing, and patch management.
– **Data Security**: Protecting data throughout its lifecycle, including encryption, access controls, backups, and secure storage solutions.
– **Identity and Access Management (IAM)**: Verifying the identity of users and controlling their access to systems and data through authentication, authorization, and management of privileges.
– **Security Awareness Training**: Educating users about cybersecurity risks and best practices to prevent social engineering attacks, such as phishing and pretexting.
– **Incident Response and Recovery**: Establishing procedures and protocols to detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents, minimizing their impact on operations and data.
4. **Cybersecurity Frameworks and Standards**: Various frameworks and standards provide guidance for organizations to develop and implement effective cybersecurity programs. Examples include NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO/IEC 27001, CIS Controls, and PCI DSS.
5. **Challenges in Cybersecurity**:
– **Cybersecurity Skills Gap**: There’s a shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, making it difficult for organizations to find and retain talent.
– **Complexity of Threat Landscape**: Cyber threats are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated, requiring continuous adaptation and investment in new technologies and strategies.
– **Interconnected Systems**: The proliferation of IoT devices and interconnected systems increases the attack surface and introduces new vulnerabilities.
– **Compliance and Regulations**: Organizations must comply with various laws and regulations related to data protection and privacy, adding complexity to cybersecurity efforts.
6. **Importance of Cybersecurity**:
– **Protection of Data**: Safeguarding sensitive information, including personal data, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets.
– **Preservation of Trust**: Maintaining trust and confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders by protecting their data and ensuring the reliability and security of digital services.
– **Prevention of Financial Loss and Reputation Damage**: Cybersecurity incidents can result in financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage for organizations.
In summary, cybersecurity is essential for protecting digital assets, ensuring the integrity and availability of data, and mitigating the risks posed by cyber threats in today’s interconnected world. It requires a holistic approach that encompasses technology, processes, people, and governance to effectively address the ever-evolving challenges of cyberspace.